A current transformer (CT) is a device that is used to measure current in an electrical system. The CT is connected in series with the circuit, and the current flowing through the circuit is measured by the CT. The output of the CT is usually in the form of a voltage which can be measured by a voltmeter.
The CT is used to protect equipment in an electrical system from overloads and faults. The CT can also be used to calculate the amount of current flowing through a circuit. There are many different types of CTs, and they are used in a variety of applications.
If you’re not familiar with current transformers, don’t worry! We’ll take a closer look at what they are, how they work, and some of the most common applications. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of current transformers and why they’re so important.
So, let’s get started! What is a current transformer, and how does it work?
What Is a Current Transformer?
Current transformers, or CTs, are an important part of electrical systems and are specifically designed to measure AC current in an electrical system. It does this by taking a current in the primary winding and transforming it into a current in the secondary winding that is proportional to the ratio of the turns of the two windings. Their purpose is to monitor the flow of electricity and send that information to a circuit breaker or other monitoring system.
They work by taking a small sample of the current in the system and transforming it into a voltage that can be read by a gauge or other electrical device. This transformation allows for the safe monitoring of large currents without cutting the power to the entire system.
Current transformers are typically used in industrial and commercial settings. They’re often found in electrical substations, where they’re used to measure the current flowing through the transmission lines. They can also be used in factories and other facilities to monitor energy usage and help optimize the power grid.
CTs are used in a variety of applications, including electrical systems in homes and businesses, as well as in large industrial systems.
How Does a Current Transformer Work?
A current transformer (CT) is a very important electrical component that is used to measure the current in an electrical circuit. You can think of it as a transformer that is specifically designed to measure current instead of voltage.

Current transformers work by taking a small sample of the current in the circuit and transforming it into a voltage. This voltage is then measured by a voltmeter and used to calculate the current in the circuit.
Current transformers are often used in conjunction with voltage transformers to create a complete transformer assembly. This assembly is then used to measure the voltage and current in an electrical system.
Well, the primary (or input) side of the transformer is connected to the source of the current that you want to measure. The secondary (or output) side is connected to the meter. When current flows through the primary side, it induces a current in the secondary side. This induced current is what is measured by the meter.
Common Applications of a Current Transformer
So, you now know the basics of what a current transformer is and how it works, but what are its applications? The main application of a current transformer is to measure the current in AC circuits or devices. It does this by providing an accurate low-current output that can be used for measuring or for other electronics.
Another common application is to monitor the overloads and short circuits in an electrical system. The current transformer senses these faults and immediately triggers alarms or shutdown the system. This helps in preventing any major power losses. Additionally, it can also be used as an isolator to protect downstream equipment from high current surges.
The most important application of a current transformer is that it helps in the efficient operation of electricity boards and devices by reducing the amount of power wasted due to overloading or underloading of currents. All in all, this device offers a range of benefits for both residential as well as industrial needs.
The Benefits of Using Current Transformers
Current transformers (CTs) are used in electrical power systems to measure alternating current (AC) in high-voltage circuits. They have several benefits, including:
Safety: CTs provide a way to measure current without directly connecting measuring instruments to high-voltage circuits, which improves safety for operators and equipment.
Isolation: CTs provide galvanic isolation between the measurement circuit and the high-voltage circuit, which helps prevent interference and damage to measurement equipment.
Accuracy: CTs can provide very accurate measurements of current, even in the presence of noise and other disturbances.
Compatibility: CTs can be used with a wide variety of measuring instruments and devices, making them compatible with many different types of power systems.
Cost-effective: CTs are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, making them a cost-effective solution for measuring current in high-voltage circuits.
The Drawbacks of Using Current Transformers
While current transformers (CTs) have many benefits, they also have some drawbacks to consider:
Limited current range: CTs typically have a limited current range, and may not be suitable for measuring very high or very low currents.
Accuracy degradation: CTs can be affected by external factors such as temperature changes, electromagnetic interference, and mechanical stress, which can cause accuracy degradation over time.
Saturation: CTs can saturate at high current levels, which can cause the output voltage to become distorted and the measurement to become inaccurate.
Maintenance: CTs require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure accurate and reliable measurements.
Installation requirement: CTs require a certain level of expertise to install, as they need to be installed in the correct location to avoid saturation and maintain accuracy, which might be a drawback if you don’t have the right know-how.
Limited frequency range: CTs are designed to work with a specific frequency range and may not be suitable for use with systems that operate at very high or very low frequencies.
It’s important to consider these drawbacks when evaluating the use of CTs in a specific application and weigh them against the benefits they provide.
Common Types and Specifications of a Current Transformer
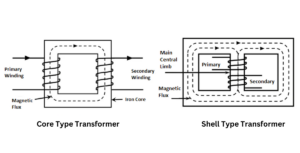
When considering the types of current transformers available, there are two common types: bar-type and window-type. The bar-type CT is a straight cylindrical core encased either in an open or an oil-filled casing. The window-type CT has an open core with a number of terminals that can be connected to external devices.
The CT’s specifications are usually provided by the manufacturer and include ratio, accuracy class, primary current rating, nominal load impedance, temperature rise, thermal capacity and impulse withstand voltage. In addition to these parameters, you must also consider the burden rating, which is the expected load that a CT should be able to handle.
Ultimately, your selection of CT should depend on what type of application it will be used for. For instance, for low-voltage applications, it would be most suitable to use a bar-type or window-type CT with lower accuracy classes due to their smaller size and cost.
On the other hand, for high voltage applications, a well-ventilated or oil-filled bar-type CT is preferable as it offers higher accuracy and insulation level ratings which ensure an accurate measurement even during extreme temperature or current variations.
Installation Considerations for Current Transformers
Before using any current transformer, it’s important to understand its proper installation considerations. This is because improper installation may lead to a wide range of problems, including inaccurate readings and potentially unsafe conditions.
To prepare for the installation process, make sure to read the instructions carefully and check the device for any electrical or structural defects. Also, it’s essential to consider the nominal power of the current transformer so that it is matched with a compatible circuit breaker.
Additionally, pay attention to the rated primary current of the device; it should match with other equipment connected in series and parallel in order to ensure properly combined measurement accuracy. When installing multiple current transformers, make sure they are located away from each other so that their magnetic fields do not interfere with each other.
By paying attention to these key factors during installation, you can ensure that your current transformer works correctly and provides accurate readings.
Common Troubleshooting Issues With Current Transformers
Routine maintenance and troubleshooting can save you from facing potential problems. Here are some issues to look out for when it comes to current transformers:
- Loose connections: Check for any loose connections in the primary and secondary windings. Make sure all connections are secure to avoid any problems.
- Failure to produce an output: This could happen due to a faulty connection or a short circuit in the transformer’s windings or because of an overload beyond what the transformer can handle.
- Unusual noise: Unusual noises like hum, crackle or squeal are usually an indication of arcing or abnormal vibrations in the transformer’s core. You may need to call in a professional if you hear this kind of noise coming from your current transformer.
Remember, proper maintenance and installation are key when it comes to avoiding any issues with your current transformer.
Adhere to Safety Standards While Using Current Transformers
It’s important to keep safety in mind when using current transformers. Just like any other electrical device, you need to take precautions to prevent accidents or other damages from occurring. Make sure you switch off the power before attempting any work on it, and make sure that all cables are securely attached.
Also, always be sure to adhere to standard safety regulations when dealing with current transformers. This includes wearing protective clothing, gloves and eye protection while handling them.
Lastly, if you’re installing these transformers in a large industrial setting, make sure you hire a qualified electrician who knows how to properly install and maintain them—in an environment like this, the smallest error could cause serious damage or injury. Taking the right safety measures won’t just keep everyone safe but also ensure that your current transformer will be around longer and work better over time.
Function and Working of a Current Transformer
A current transformer (CT) is an instrument transformer that is used to measure electrical current in a power system. It functions by providing a current in its secondary winding that is proportional to the current flowing in its primary winding. This allows for accurate measurement of the current in the primary circuit, which is often at a high voltage level, without the need for direct contact with the high voltage. The primary winding of a CT is connected in series with the current-carrying conductor in the power system, while the secondary winding is connected to the measuring instrument. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to the number of turns in the secondary winding is used to calculate the current in the primary circuit. CTs are widely used in power system protection and monitoring applications.
Applications of a Current Transformer
You may be wondering about all the different ways current transformers are used. Quite simply, they are used for measuring purposes in AC systems. They can be used to measure voltage and current levels in a circuit, as well as fault currents and power factors.
Current transformers can also be used in protection systems to regulate overcurrents and short circuits. They help to protect the system from overloads by providing accurate measurements of currents that are too high. In particular, they often come into play when it comes to overcurrent protection for electronic systems used in industrial environments.
In addition, current transformers can be employed for metering applications where you need to monitor the amount of energy you’re using in your home or business. This can help you save money in the long run by becoming aware of how much electricity you’re consuming each day.
So, that’s all there is to know about current transformers – their function, working, and applications! With this comprehensive guide, you should now have a better understanding of what it is and how it’s being used in both residential settings and industrial environments.
Conclusion
So, if you are in the market for a current transformer, be sure to keep the above-mentioned points in mind. When it comes to current transformers, it’s important to understand the different types and how they work. You should also be familiar with the different applications they’re used for, so you can choose the right one for your needs.
If you are still unsure about which product to select, do not hesitate to get in touch with the experts at Grant Transformers. We would be more than happy to help you find the perfect transformer for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Current Transformers
You may have some questions about the current transformer and its uses. Here are some of the most frequently asked ones.
Q. What’s the difference between a current transformer and a power transformer?
A. The main difference is that current transformers measure the amount of electric current passing through a specific wire, while power transformers can either increase or decrease voltage levels in an electrical system.
Q. How are current transformers used?
A. Current transformers are used to measure and control the electric current in circuits, systems, and equipment. They can also be used to provide over-current protection, as well as to monitor the performance of circuits and devices such as motors, generators, and batteries.
Q. What Is the Function of a Current Transformer?
A. A current transformer, or CT, is a device used to measure electric current. It does this by transforming a high current into a lower one, which is easier to measure. This is why CTs are often used in electrical substations to measure the amount of electricity flowing through the power lines.
Without a current transformer, the technicians at these substations would have to use a megger to test the current. This is a very time-consuming process, and it’s not always accurate. By using a current transformer, the technicians can quickly and easily get an accurate reading of the current flowing through the power lines.
Q. Can I use a current transformer for measuring voltage?
A. No; current transformers are designed to measure only electric currents, not voltages.
Q. What are the different types of current transformers?
A. There are three main types of current transformers:
1) The first type is the standard current transformer. As the name suggests, this is the most common type of current transformer and is used in a wide range of applications.
2) The second type is the Rogowski coil current transformer. This type of current transformer is often used in high-voltage applications as it can handle large currents without any loss of accuracy.
3) The third type is the split-core current transformer. This type of transformer is designed to be easily installed on existing cables and wires, making it a popular choice for industrial applications.