If you live in a house or an apartment that gets its electricity from a standard outlet, you’re probably fine, especially if you have common electronic appliances that don’t consume or require unusual amounts of voltage.
What if you’ve just started a business that relies on heavy machinery? A step-up transformer will be required.
These transformers go above and beyond standard electrical outlets to provide high-voltage electricity for appliances and equipment based on their required power consumption. A step-up transformer is required if you intend to run your computer, refrigerator, washer and dryer, and other electrical appliances.
A step-up transformer may also be required in other situations. Let’s go over everything you should know about step-up transformers.
What is a step-up transformer?
A step-up transformer is a device that converts low-voltage electricity to high-voltage.
Step-up transformers are used for various reasons, the most common of which is to provide adequate power to large appliances and equipment.
Your refrigerator, for example, may require 200 volts of power. If you plug it into a 120-volt outlet, your refrigerator may not function properly.
This can be fixed with a step-up transformer.
Step-up transformers aren’t just for big-ticket items like refrigerators. They are also used for small household items such as computers, lamps, radios, etc.
They are also used in businesses to power medium to heavy industrial equipment and machinery such as welders and metal-cutting machines.
Construction and components of step-up transformers
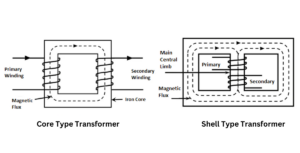
The magnetic induction principles are used by the step-up transformer. It is made up of two major parts: the core and the windings.
Manufacturers of step-up electrical transformers use a highly permeable substance at the core to allow magnetic current to flow without wasting much of it. The magnetic flux lines will be limited by the core due to the strong core material. As a result, transformer waste is reduced, resulting in increased operational efficiency. Core heating is reduced by laminating the core to hold the eddy current, resulting in less waste.
Windings are in charge of transferring electric current. Most transformer manufacturers create high-quality windings to keep the transformer cool and to withstand high temperatures. The primary coil winding density is high, but the number of turns is low.
In contrast, the secondary coil winding density is thin but contains more turns. As a result, the secondary side has more energy than the primary side, resulting in higher voltage transfer. Copper and aluminum can both be used in the coil. While aluminum is less expensive, copper extends the life of a transformer significantly.
How does a step-up transformer work?
The step-up transformer works on a simple principle. However, depending on the direction of the current flow, it can also function as a step-down transformer. The output value of the step-up transformer is greater than the input value. As alternating current flows across the step-up power transformer, it transforms in one direction, then stops and changes direction to transform into another.
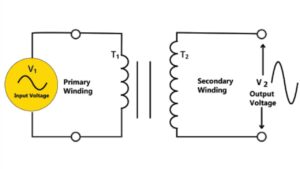
In the winding area, the flow of current creates a magnetic flux. When the current flow changes direction, the magnetic poles change direction as well. The magnetic field generates the voltage in the windings.
Similarly, the mutual induction effect refers to the voltage produced across the secondary winding when it is located in a moving magnetic flux. As a result, the AC generates a moving magnetic flux in the primary winding, allowing voltage to be built in the secondary winding.
Most electrical transformer manufacturers create step-up transformers for generator step-up devices, which are found in all power plants.
The Main Function of Step-up Transformer
A step-up transformer is one of several types of transformers. The function of the step-up transformer is to increase voltage compensation. As a result, it is also known as the step-up compensator. The step-up transformer has the ability and performance to start and increase voltage quickly. In fact, most transformers are classified as step-up or step-down depending on whether the voltage is increased or decreased. In terms of voltage, the two types of transformers are diametrically opposed. In the case of a step-up transformer, the secondary coil has more turns than the primary coil, whereas, in the case of a step-down transformer, the secondary coil has fewer turns than the primary coil.
The step-up transformer is a type of isolation transformer that comes in single-phase and three-phase configurations. The transformer has a small volume, high quality, and good performance with voltage classes ranging from 220V, 380V, 400V, 415V, 480V, 500V, 515V, 660V, 690V, 1140V, and 60KV. Its body is made of silicon, steel sheets, and oxygen-free copper wire. The product is widely used in a variety of situations, such as construction and engineering lines. Furthermore, it can compensate for the insufficient voltage caused by the difference between the voltage with different classes at home and the imported matching equipment.
Working with Step-Up Transformers
These step-up transformers use electromagnetic induction principles to convert AC power from a lower voltage to a higher voltage. The transformer is made up of two or more windings or wire coils. They are also separated by a ferromagnetic core material. When an alternating current is applied to a winding, it produces a changing magnetic field, which causes a voltage in another winding. The transformation ratio, and thus the transformer’s output voltage, is determined by the ratio of the number of turns in the two windings.
The efficiency of a step-up transformer is one of the most noticeable factors in its performance. Furthermore, the efficiency of the transformer indicates the percentage of input power that is transformed into useful output power rather than being wasted as heat. Improving transformer efficiency can help to reduce energy costs while also extending the life of the transformers.
Step-up transformers must be optimised for performance and reliability if they are to be successful. This blog post will go over some pointers and tricks for taking your step-up transformers to the next level.
1. Select the best transformer for the job!
Choosing the right transformer for a specific application is one of the most important factors in the success of a step-up power transformer. This includes taking into account things like:
- Power and voltage ratings
- AC current frequency
- The amount of available space
- The environment in which it will operate
- Operation types
- Observance of regulations
2. Installation and commissioning procedures must be followed correctly
Step-up power transformers are dependable and efficient. Proper installation and commissioning procedures must be followed. Manufacturers of step-up transformers provide installation and testing instructions. Certainly, these instructions can be followed to ensure that transformers work properly.
3. Using high-quality materials
The use of high-quality components can help to improve a step-up power transformer’s performance and reliability. This includes using high-quality materials, such as high-quality insulation and conductors, as well as selecting components that are designed to withstand the transformer’s specific operating conditions.
4. Improve the transformer design
A transformer’s design can improve efficiency. This includes optimising the number of turns in the windings, the core size and shape, and the winding layout. Engineers can make necessary changes to the design of a transformer using the most recent and advanced computer simulations and modelling techniques to achieve the highest possible efficiency.
5. Application of advanced cooling techniques
The heat generated by a transformer can reduce its efficiency and shorten its lifespan. The heat generated by the transformer is dispersed using advanced cooling techniques. This could also include using air-forced cooling, water cooling, or other cooling methods.
6. Maintain your equipment on a regular basis!
A step-up power transformer must be serviced on a regular basis to ensure that it operates reliably and effectively. This could include cleaning the transformer, checking the oil level and quality, and testing the insulation. Furthermore, keeping records of all maintenance activities and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is essential.
7. Keep an eye out for signs of failure
Step-up power transformers can fail for a variety of reasons. Overheating, electrical stress, and mechanical stress are all examples of this. It is critical to monitor the transformer on a regular basis to detect any signs of failure. It can assist in taking action if any problems are detected. This could include replacing damaged components or performing necessary repairs.
8. Use safety equipment!
For instance, Circuit breakers and fuses can aid in the prevention of step-up transformer damage. It is critical to use these devices and ensure that they are appropriately sized and rated for the application.
Step-up power transformers are vulnerable to a number of potential hazards. Overloading, short circuits, and lightning strikes are examples of this. Advanced protection and monitoring devices, on the other hand, detect and respond to these dangerous events.
9. Transformers must be stored and transported with care
Step-up transformer manufacturers must ensure proper storage and transportation. Without a doubt, this could reduce the damage and be ready to use when needed. To protect the transformer from external factors, step-up transformer manufacturers should use proper handling equipment such as cranes and dollies.
Step-up transformers: why use them?
Step-up transformers are widely used in both residential and commercial applications. They are widely used in power plants and commercial settings to regulate voltage fluctuations and power various electrical devices. Here are some reasons why you should use step-up transformers:
The step-up transformer has a quick start feature. There’s no need to set up a slew of procedures before turning on the transformer.
Because there is little load on the primary windings, which can become damaged over time, the transformer requires little maintenance.
Step-up power transformers have high-efficiency ratings and do not waste energy when the current is flowing.
Step-up transformers are most commonly used in power distribution. They are used to reduce energy waste that travels for miles before reaching a residential or commercial property.
A high-quality step-up transformer boosts voltage while stabilising current flow. They are necessary for power generation because energy can easily flow over long distances. Step-up transformers are ideal for heavy-duty electrical appliances and industrial equipment.
The Benefits of Step-Up Transformers
Here are the top five compelling reasons to buy and use a step-up transformer:
1. Allows for smooth power transmission
Power transmission over long distances is made possible by step-up transformers. It also aids in lowering the loss factor caused by voltage drop.
2. It does away with the need for additional power supplies
A step-up transformer raises the voltage of a power source. It can be used to boost a low voltage to a higher level without the need for a separate power supply. As a result, no additional power supplies are required.
3. Highly dependable and long-lasting
Step-up transformers, unlike other types of transformers, are extremely dependable and long-lasting. They are designed with high-quality materials and components, which makes them withstand longer periods without any issues or damage. They also contribute to long-term performance by ensuring stable power output over a longer period of time. This is accomplished by ensuring adequate insulation between windings to prevent overheating or damage from excessive current flow through them.
4. Constant and continuous effort
Let’s face it: very few electronics can run continuously without being turned off. This is not the same as a step-up transformer. It is designed to run continuously without being turned off and to always be ready to produce the required voltage.
This is extremely beneficial in a variety of ways. It saves energy because it does not require the use of a power supply that must be turned on and off. The continuity factor also has an impact on the step-up transformer’s reliability and efficiency.
5. Various applications
A step-up transformer is not only useful for powering applications such as computers, televisions, and game consoles, but it can also be used to power lighting, appliances, electric motors, and other devices.
The fact that the step-up transformer can be used in both residential and industrial applications contributes to its widespread use. This means you can use the transformer both at work and at home.
Step Up Transformers vs Step Down Transformers
The primary function of a step-up transformer is to convert (transform) a lower primary voltage to a higher secondary voltage. This is frequently the case on construction sites where 480 volts is required to power large industrial equipment. In addition, to save energy, industrial warehouses and other industrial buildings incorporate step-up transformers into their distribution systems to power industrial-scale LED lighting fixtures and high bays.
To put it simply, a step-down transformer operates in the inverse direction of a step-up transformer. Its primary function is to transform a higher primary voltage into a lower secondary voltage. This will frequently convert 277/480V to standard 120/208V for use with power tools and temporary lighting throughout the job site or entertainment venue.
Although the key differences between step-up and step-down transformers are obvious, there are some additional details worth exploring. Step-up transformers, for example, have low-voltage primary windings and high-voltage secondary windings. Step-down transformers, on the other hand, have high-voltage primary windings and low-voltage secondary windings.
However, when looking for the best portable transformer, the most important factor to consider is how step-up and step-down options raise and lower voltage levels, respectively. Voltage levels are increased by step-up transformers and decreased by step-down transformers.
Summary
As a result, this is all about the step-up transformer concept. The step-up form’s performance is to increase the voltage while decreasing current strength. When compared to the primary side, this type has a large number of coils across the secondary section. As a result, the wire in the primary winding is stronger than the wire in the secondary winding. These devices are critical in transmission and power generation networks because they transport energy to remote locations.